Features of 8255:
•It has three 8-bit ports
•It can be operated in three different modes in I/O mode and in BSR mode
IC 8255 has three ports A, Band C. The ports A and B are 8 bit parallel ports. Port A can be programmed to work in any one of the three modes as input or output port. The three operating modes are
Mode-0 - Simple I/O port
Mode-l - Handshake I/O port
Mode-2 - Bidirectional I/O port.
The port B can be programmed to work either in mode-0 or mode-1. The port C pins (8-pins) have different assignments depending on the mode of port A and B. If port A and B are programmed in mode-0, then the port C can perform anyone of the following function.
1. As 8 bit parallel port in mode-0 for input or output.
2. As two numbers of 4 bit parallel port in mode-O for input or output.
3. The individual pins of port C can be set or reset for various control applications.
The various functions (assignments) of port C during the different operating modes of port A and B are listed in Table below.
If ports A and Bare programmed in mode-l or mode-2, then some of the pins of port C are used for handshake signals and the remaining pins can be used as input/output lines or individually set/reset for control applications.
I/0 Modes of 8255
Mode-0: In this mode, all the three ports can be programmed either as input or output port. In mode-O, the outputs are latched and the inputs are not latched. The ports do not have handshake or Interrupt capability. The ports in mode-o can be used to interface DIP switches, Hexa-keypad, LED's and 7-segment LED's to the processor.
Mode-l: In this mode, only ports A & B can be programmed either as input or output port. In mode-1, handshake signals are exchanged between the processor and peripherals prior to data transfer. The port C pins are used for handshake signals. Input and output data are latched. Interrupt driven data transfer scheme is possible.
8255 Handshake Input port (Mode 1)
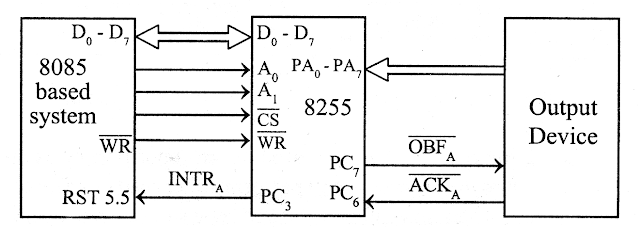
8255 Handshake Output port (Mode 1)\
Mode-2: In this mode, the port will be a bi-directional port (i.e., the processor can perform both read and write operations with an I/O device connected to a port in mode-2).
Only port-A can be programmed to work in mode-2. Five pins of port C are used for handshake signals. This mode is used primarily in applications such as data transfer between two computers or floppy disk controller interface.
Pins & Signals of 8255
The pin description of 8255 is shown in figure below. It has 40 pins and requires a single +5V supply.




No comments:
Post a Comment