Electrical and Electronics Engineering Portal!
Bit Manipulation Instruction Set (Logical Instructions) In 8086 Processors
Eg. : ; AL = 0110 1100
NOT AL ; AL = 1001 0011
; CX = 10101111 0010 0010
NOT CX ; CX = 0101 0000 11011001
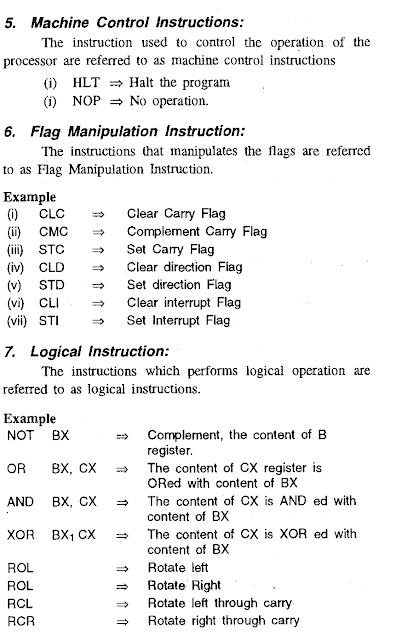
AND: This instruction logically ANDs each bit of the source byte or word with the corresponding bit in the destination and stores result in the destination.
Eg. : ; AL = 1001 0011 = 93H
; BL = 0111 0101 = 75H
AND BL, AL ; AND Byte in AL with byte in BL
; BL = 0001 0001 = 11H
OR : This instruction logically ORs each bit of the source byte or word with the corresponding bit in the destination and stores result in the destination.
Eg. : ; AL =1001 0011 = 93H
; BL =0111 0101 = 75H
OR BL, AL ; OR byte in AL with byte in BL
; BL =1111 0111 = F7H
XOR : This instruction logically XORs each bit of the source byte or word with the corresponding bit in the destination and stores result in the destination.
TEST: This instruction logically ANDs each bit of the source byte or word with the corresponding bit in the destination and updates the flags but not stores results in anywhere.
Eg. : ; AL = 1001 0011 = 93H
; BL = 0111 0101 = 75H
AND BL, AL ; AND Byte in AL with byte in BL
; Result = 0001 0001 = 11H (not stored)
; Z = 0, P = 1 (flag affected))
AND BX, AX ; AND word in AX with word in BX
; updates the flag and result is not stored.
Arithmetic Instruction Set In 8086 Processors
Labels:
8086 – ARCHITECTURE,
8086 PIN CONFIGURATION,
80X86 PROCESSORS,
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMME OF 80X86 PROCESSORS,
Data Transfer Instructions In 8086 Processors,
INTEL 8255,
MAXIMUM MODE CONFIGURATION OF 8086 SYSTEM,
MINIMUM MODE CONFIGURATION OF 8086 SYSTEM
Data Transfer Instruction Set In 8086 Processors
The instructions that transfer data between registers, memory locations or segment registers.
It is again classified into four types. They are,
It is again classified into four types. They are,
1.General purpose byte or word transfer instructions
2.Special address transfer instructions
3.Flag transfer instructions
4.Simple input and output Port transfer instructions
1.General purpose byte or word transfer instructions
MOV: It copies the content of source to the destination.
Eg. : MOV BX, 5978H ; Load the immediate number 5978H to BX.
MOV CL, [453AH] ; Copies the content of memory location which is at a distant of 453AH from the data segment into CL register.
MOV DS, CX ; Copies the word from CX to data segment.
PUSH
• It decrements the stack pointer by 2.
• It stores the 16 bit data from the source to the address in the stack pointer.
Eg. : SP = 80983H
CX = 49A3H
PUSH CX
SP = 80981H
[CX]----> SP
POP
•It stores the 16 bit data from the destination to the stack pointer.
•It increments the stack pointer by 2.
Eg. : SP = 80983H
CX = 49A3H
POP CX
[CX]
SP = 80985H
XCHG: It exchanges the contents of source with the destination.
Eg. : XCHG BX, CX ; Exchange word in CX with word in BX.
XCHG BL, CL ; Exchange byte in CL with byte in BL.
XLAT :
•IT replaces byte in AL register.
•BX is having the offset value of memory location.
•It copies byte from address pointed by [BX + AL ] into AL register.
2. Special address transfer instructions:
LEA:
•Load effective address.
•The mnemonics is LEA register, source.
•Source is having the offset of the memory location and this instruction load this address into 16 bit register.
LDS:
•The mnemonics is LDS register, memory address of first word.
•It copies a word from two memory locations into the register.
•It then copies a word from next two memory locations into the DS register.
Eg. : LDS CX, [391AH]
LES:
• The mnemonics is LES register, memory address of first word.
• It copies a word from two memory locations into the register.
• It then copies a word from next two memory locations into the ES register.
Eg. : LES CX, [391AH]
3. Flag Transfer Instructions:
LAHF : This instruction copies the contents of lower byte of 8086 flag register to AH register.
SAHF : The contents of the AH register are copied into the lower byte of the 8086 flag register.
PUSHF: This instruction decrements the stack pointer by 2 and copies the word in the flag register to the memory locations pointed by the stack pointer.
POPF : This instruction copies a word the two memory locations at the top of the stack to the flag register and increments the stack pointer by 2.
4. Simple Input and Output Port Transfer Instructions:
IN :
•This instruction will copy data from a port to the accumulator.
•If an 8 bit port is read the data will go to AL and if an 16 bit port is read the data will go to AX.
OUT : The OUT instruction copies a byte from AL or a word from AX to the specified port.
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMME OF 80X86 PROCESSORS
The general format of an assembler instruction is,
Label: Mnemonics Operand, Operand; comment.
8086 instruction set is classified as follows.
4.String instruction.
5.Program execution transfer instruction.
6.Processor control instruction.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Labels
PROJECTS
8086 PIN CONFIGURATION
80X86 PROCESSORS
TRANSDUCERS
8086 – ARCHITECTURE
Hall-Effect Transducers
INTEL 8085
OPTICAL MATERIALS
BIPOLAR TRANSISTORS
INTEL 8255
Optoelectronic Devices
Thermistors
thevenin's theorem
MAXIMUM MODE CONFIGURATION OF 8086 SYSTEM
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMME OF 80X86 PROCESSORS
POWER PLANT ENGINEERING
PRIME MOVERS
8279 with 8085
MINIMUM MODE CONFIGURATION OF 8086 SYSTEM
MISCELLANEOUS DEVICES
MODERN ENGINEERING MATERIALS
8085 Processor- Q and A-1
BASIC CONCEPTS OF FLUID MECHANICS
OSCILLATORS
8085 Processor- Q and A-2
Features of 8086
PUMPS AND TURBINES
8031/8051 MICROCONTROLLER
Chemfet Transducers
DIODES
FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
METHOD OF STATEMENTS
8279 with 8086
HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING
OVERVOLATGES AND INSULATION COORDINATION
Thermocouples
8251A to 8086
ARCHITECTURE OF 8031/8051
Angle-Beam Transducers
DATA TRANSFER INSTRUCTIONS IN 8051/8031
INSTRUCTION SET FOR 8051/8031
INTEL 8279
KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY INTERFACES USING 8279
LOGICAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR 8051/8031
Photonic Transducers
TECHNOLOGICAL TIPS
THREE POINT STARTER
8257 with 8085
ARITHMETIC INSTRUCTIONS IN 8051/8031
LIGHTNING PHENOMENA
Photoelectric Detectors
Physical Strain Gage Transducers
8259 PROCESSOR
APPLICATIONS OF HALL EFFECT
BRANCHING INSTRUCTIONS FOR 8051/8031
CPU OF 8031/8051
Capacitive Transducers
DECODER
Electromagnetic Transducer
Hall voltage
INTEL 8051 MICROCONTROLLER
INTEL 8251A
Insulation Resistance Test
PINS AND SIGNALS OF 8031/8051
Physical Transducers
Resistive Transducer
STARTERS
Thermocouple Vacuum Gages
USART-INTEL 8251A
APPLICATIONs OF 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
CAPACITANCE
Data Transfer Instructions In 8086 Processors
EARTH FAULT RELAY
ELECTRIC MOTORS
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS
ELECTRICAL BREAKDOWN IN GASES
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET)
INTEL 8257
IONIZATION AND DECAY PROCESSES
Inductive Transducers
Microprocessor and Microcontroller
OVER CURRENT RELAY
OVER CURRENT RELAY TESTING METHODS
PhotoConductive Detectors
PhotoVoltaic Detectors
Registers Of 8051/8031 Microcontroller
Testing Methods
ADC INTERFACE
AMPLIFIERS
APPLICATIONS OF 8259
EARTH ELECTRODE RESISTANCE MEASUREMENT TESTING METHODS
EARTH FAULT RELAY TESTING METHODS
Electricity
Ferrodynamic Wattmeter
Fiber-Optic Transducers
IC TESTER
IC TESTER part-2
INTERRUPTS
Intravascular imaging transducer
LIGHTNING ARRESTERS
MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
Mechanical imaging transducers
Mesh Current-2
Millman's Theorem
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
Norton's
Polarity Test
Potentiometric transducers
Ratio Test
SERIAL DATA COMMUNICATION
SFR OF 8051/8031
SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS
Speed Control System 8085
Stepper Motor Control System
Winding Resistance Test
20 MVA
6-digits
6-digits 7-segment LEDs
7-segment
A-to-D
A/D
ADC
ADVANTAGES OF CORONA
ALTERNATOR BY POTIER & ASA METHOD
ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER
AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER
AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER TESTING
AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER TESTING METHODS
Analog Devices
A–D
BERNOULLI’S PRINCIPLE
BUS BAR
BUS BAR TESTING
Basic measuring circuits
Bernoulli's Equation
Bit Manipulation Instruction
Buchholz relay test
CORONA POWER LOSS
CURRENT TRANSFORMER
CURRENT TRANSFORMER TESTING
Contact resistance test
Current to voltage converter
DAC INTERFACE
DESCRIBE MULTIPLY-EXCITED
Digital Storage Oscilloscope
Display Driver Circuit
E PROMER
ELPLUS NT-111
EPROM AND STATIC RAM
EXCITED MAGNETIC FIELD
Electrical Machines II- Exp NO.1
Energy Meters
FACTORS AFFECTING CORONA
FLIP FLOPS
Fluid Dynamics and Bernoulli's Equation
Fluorescence Chemical Transducers
Foil Strain Gages
HALL EFFECT
HIGH VOLTAGE ENGG
HV test
HYSTERESIS MOTOR
Hall co-efficient
Hall voltage and Hall Co-efficient
High Voltage Insulator Coating
Hot-wire anemometer
How to Read a Capacitor?
IC TESTER part-1
INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS
Importance of Hall Effect
Insulation resistance check
Insulator Coating
Knee point Test
LEDs
LEDs Display Driver
LEDs Display Driver Circuit
LM35
LOGIC CONTROLLER
LPT
LPT PORT
LPT PORT EXPANDER
LPT PORT
LPT PORT EXTENDER
Life Gone?
MAGNETIC FIELD
MAGNETIC FIELD SYSTEMS
METHOD OF STATEMENT FOR TRANSFORMER STABILITY TEST
METHODS OF REDUCING CORONA EFFECT
MULTIPLY-EXCITED
MULTIPLY-EXCITED MAGNETIC FIELD SYSTEMS
Mesh Current
Mesh Current-1
Moving Iron Instruments
Multiplexing
Network Theorems
Node Voltage Method
On-No Load And On Load Condition
PLC
PORT EXTENDER
POTIER & ASA METHOD
POWER TRANSFORMER
POWER TRANSFORMER TESTING
POWER TRANSFORMER TESTING METHODS
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLER
Parallel Port EXPANDER
Paschen's law
Piezoelectric Wave-Propagation Transducers
Potential Transformer
RADIO INTERFERENCE
RECTIFIERS
REGULATION OF ALTERNATOR
REGULATION OF THREE PHASE ALTERNATOR
Read a Capacitor
SINGLY-EXCITED
SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS Classical gas laws
Secondary effects
Semiconductor strain gages
Speaker Driver
Strain Gages
Streamer theory
Superposition
Superposition theorem
Swinburne’s Test
TMOD
TRANSFORMER TESTING METHODS
Tape Recorder
Three-Phase Wattmeter
Transformer Tap Changer
Transformer Testing
Vector group test
Virus Activity
Voltage Insulator Coating
Voltage To Frequency Converter
Voltage to current converter
What is analog-to-digital conversion
Windows work for Nokia
capacitor labels
excitation current test
magnetic balance
voltage to frequency converter wiki electronic frequency converter testing voltage with a multimeter 50 hz voltages voltmeter